The Science Behind HIIT: Why It’s the Ultimate Fat-Burning Workout
The Benefits of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)

High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) offers a multitude of advantages for both fitness enthusiasts and those looking to improve their health. One of the key benefits of HIIT is its ability to efficiently burn calories in a shorter amount of time compared to traditional steady-state cardio. By incorporating short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods, HIIT helps to elevate the heart rate and increase calorie expenditure both during and after the workout.
Additionally, HIIT has been shown to enhance cardiovascular fitness, making it an effective method for improving overall heart health. This type of training can lead to increased endurance, improved oxygen utilization, and better circulation, all of which contribute to a stronger cardiovascular system. Moreover, the versatility of HIIT allows individuals to customize their workouts to their fitness level and goals, making it a flexible and time-efficient option for enhancing physical fitness.
How HIIT Works to Burn Fat
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is renowned for its ability to torch fat efficiently. This workout method pushes the body to its limits through short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods. The high intensity of HIIT workouts elevates the heart rate and stimulates the body to burn calories during and after the workout. This post-exercise calorie burn, known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), plays a key role in fat loss as the body works to restore itself to its pre-exercise state.
Moreover, the intensity of HIIT triggers the body to tap into its fat stores for energy, leading to increased fat oxidation. This metabolic adaptation occurs during HIIT sessions and continues post-workout, allowing individuals to continue burning calories even after they have finished exercising. Additionally, HIIT has been shown to preserve muscle mass while reducing body fat, making it a valuable tool for those looking to improve their body composition and enhance fat loss.
The Role of Metabolism in HIIT
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has gained popularity for its ability to boost metabolism both during and after workouts. This form of exercise involves short bursts of intense activity followed by brief periods of rest or lower-intensity exercise. Research shows that HIIT can increase the body’s energy expenditure post-exercise, leading to a higher metabolic rate throughout the day. This effect, known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), results in the body burning more calories even when at rest.
One of the key mechanisms through which HIIT impacts metabolism is by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). HIIT has been shown to stimulate the production of new mitochondria in muscle cells, enhancing their capacity to produce energy. This increase in mitochondrial density not only improves athletic performance but also plays a crucial role in enhancing metabolism and promoting fat oxidation.
The Afterburn Effect of HIIT
The afterburn effect of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is a key element that distinguishes it from traditional steady-state cardio. This phenomenon, scientifically known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), refers to the increased oxygen intake following an intense workout to restore the body to its pre-exercise state. During this period, the body continues to burn calories at an elevated rate, even after the workout has ended. HIIT has been shown to induce a more significant afterburn effect compared to steady-state cardio, making it an efficient method for maximizing calorie expenditure and fat loss.
Research suggests that the afterburn effect of HIIT can last for several hours post-workout, contributing to overall energy expenditure. This extended calorie-burning period is attributed to the intense bursts of activity during HIIT, which elevate the heart rate and demand more energy from the body. The combination of high-intensity intervals followed by brief recovery periods challenges the cardiovascular system and muscles, leading to a heightened metabolic rate that persists well beyond the workout session. By incorporating HIIT into your fitness routine, you can take advantage of this afterburn effect to enhance fat loss and improve overall metabolic efficiency.
How HIIT Increases EPOC
HIIT, known for its effectiveness in burning calories long after the workout is completed, is able to significantly increase EPOC, or Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption. This phenomenon, often referred to as the afterburn effect, describes the elevated rate of oxygen intake post-exercise to aid in the body’s recovery process. HIIT workouts, characterized by repeated bursts of high-intensity exercise followed by short recovery periods, create a metabolic demand that requires additional oxygen consumption after the workout is finished. As a result, EPOC is elevated for an extended period, leading to increased calorie expenditure even while at rest.
The intensity and challenge that HIIT poses on the body during the workout play a crucial role in the elevation of EPOC. The high-intensity intervals push the body to work harder, depleting energy stores and creating a significant demand for oxygen during and after the workout. This increased demand triggers various physiological responses, such as the restoration of oxygen levels, replenishment of energy stores, and repair of muscle tissue damaged during the intense exercise, all contributing to the heightened EPOC. Ultimately, the combination of intense exercise and the body’s post-workout recovery processes leads to a prolonged afterburn effect that can enhance the overall calorie burn and metabolic rate over time.
The Science of HIIT and Muscle Building
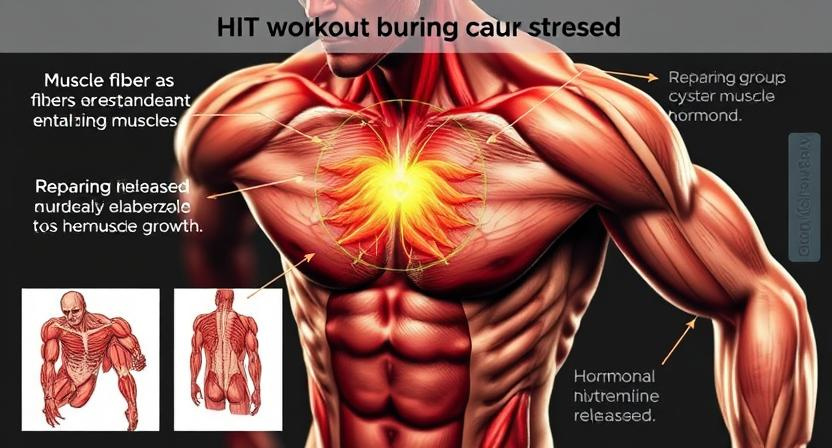
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has gained popularity not only for its fat-burning benefits but also for its effects on muscle building. The science behind HIIT and muscle building lies in its ability to stimulate muscle protein synthesis and promote muscle growth. During HIIT workouts, the fast-twitch muscle fibers are recruited, leading to micro-tears in the muscle fibers. As the body repairs these micro-tears during the recovery phase, muscle protein synthesis is stimulated, resulting in muscle growth.
Moreover, HIIT triggers the release of growth hormone and testosterone, which are essential for muscle building. The high-intensity nature of HIIT causes a significant metabolic stress on the body, leading to greater energy expenditure and an increase in muscle mass. Additionally, HIIT workouts can be customized to target specific muscle groups, allowing individuals to tailor their training to achieve their muscle-building goals effectively.
HIIT vs. Steady-State Cardio for Fat Loss
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and steady-state cardio are two popular forms of exercise often compared for their effectiveness in fat loss. HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief periods of rest or lower intensity activity. This type of training is known to elevate the heart rate quickly and effectively burn calories during and even after the workout, due to the phenomenon known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC).
On the other hand, steady-state cardio involves maintaining a consistent moderate intensity level of exercise, such as jogging or cycling, for an extended period of time. While steady-state cardio can also help burn calories during the workout, it typically does not have the same post-exercise calorie burning effects as HIIT. HIIT has been shown to be more time-efficient and potentially more effective for fat loss compared to steady-state cardio, making it a popular choice for those looking to maximize their fat-burning potential.
The Impact of HIIT on Insulin Sensitivity
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has been shown to have a positive impact on insulin sensitivity in individuals. Insulin sensitivity refers to how effectively the body’s cells respond to insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. Studies have indicated that regular HIIT sessions can lead to improvements in insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to regulate blood sugar levels and potentially reducing the risk of developing conditions like type 2 diabetes.
One of the key mechanisms through which HIIT improves insulin sensitivity is by promoting the uptake of glucose by skeletal muscle cells. During HIIT workouts, the muscles require a higher demand for energy, leading to an increased sensitivity to insulin and enhanced glucose uptake. This process can help improve overall blood sugar control and lower the risk of insulin resistance, highlighting the importance of incorporating HIIT into fitness routines for individuals looking to enhance their metabolic health.
How HIIT Improves Cardiovascular Health
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has been shown to significantly improve cardiovascular health by enhancing heart function and increasing the efficiency of the cardiovascular system. Through the intense bursts of activity followed by short recovery periods, HIIT can help to strengthen the heart muscle, improve blood flow, and boost overall cardiovascular endurance. This form of exercise can also lead to a reduction in resting heart rate and blood pressure, both of which are important indicators of heart health.
Moreover, HIIT has been found to positively impact various cardiovascular risk factors, such as cholesterol levels and vascular function. Studies have demonstrated that HIIT can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels, and improve the function of blood vessels. By incorporating HIIT into a regular fitness routine, individuals can effectively enhance their cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of developing heart-related diseases.
The Effect of HIIT on Hormones
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has been shown to have a significant impact on hormone levels in the body. Research has demonstrated that HIIT can lead to an increase in the production of hormones such as adrenaline and growth hormone. These hormones play crucial roles in fat metabolism, muscle growth, and overall metabolic function. The intense nature of HIIT workouts is believed to trigger a hormonal response that helps optimize the body’s ability to burn fat and build lean muscle mass.
Additionally, HIIT has been found to have a positive effect on insulin sensitivity, which is the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. By incorporating HIIT into a fitness routine, individuals may experience improvements in insulin sensitivity, leading to better blood sugar control and reduced risk of conditions such as diabetes. The hormonal changes induced by HIIT workouts can contribute to enhanced overall health and well-being, making it a valuable addition to any fitness regimen.
The Relationship Between HIIT and Resting Metabolic Rate
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has been shown to have a positive impact on resting metabolic rate (RMR). RMR is the number of calories your body burns at rest to maintain basic physiological functions. Studies suggest that HIIT can elevate RMR for up to 24 hours post-exercise, meaning you continue to burn calories even after your workout is done.
One of the reasons HIIT is effective at increasing RMR is the intense bursts of activity followed by short recovery periods, which create a metabolic disturbance in the body. This disturbance requires energy for recovery and repair, leading to an increase in calorie expenditure. By challenging your body in this way, HIIT stimulates metabolic adaptations that can result in a higher RMR over time.
The Importance of Intensity in HIIT Workouts

High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is known for its effectiveness in improving cardiovascular fitness and burning fat due to its emphasis on intensity. Intensity in HIIT workouts refers to the level of effort exerted during each interval of high-intensity exercise. By pushing your body to perform at maximum capacity during short bursts of exercise followed by brief rest periods, you can maximize the benefits of HIIT. It is this intensity that sets HIIT apart from traditional steady-state cardio exercises and makes it a time-efficient and powerful workout option.
The key to reaping the full benefits of HIIT lies in maintaining a high level of intensity throughout the workout. When you push yourself to perform at a high intensity, you not only burn more calories during the workout itself but also continue to burn calories at an elevated rate after the workout is over. This post-exercise calorie burn, known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), is heightened by the intense nature of HIIT workouts. By incorporating intervals of high intensity into your training regimen, you can challenge your body in new ways and achieve greater results in a shorter amount of time.
The Connection Between HIIT and Fat Oxidation
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has been shown to be highly effective in promoting fat oxidation in the body. During HIIT workouts, the intense bursts of activity engage different energy systems, leading to an increased demand for oxygen post-exercise. This heightened oxygen consumption, known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), plays a crucial role in enhancing fat oxidation even after the workout is completed.
Furthermore, HIIT promotes the activation of enzymes involved in fat oxidation and metabolic processes. This increased enzyme activity not only facilitates the breakdown of fatty acids but also improves the body’s ability to utilize fat as a fuel source during rest and physical activity. As a result, individuals engaging in regular HIIT sessions may experience greater fat loss and improvements in body composition compared to traditional steady-state cardio exercises.
The Influence of HIIT on Appetite Regulation
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has been shown to play a significant role in appetite regulation. Studies suggest that HIIT sessions may help regulate hunger hormones, such as ghrelin and leptin, leading to a decrease in overall appetite. The intense nature of HIIT workouts can also impact post-exercise appetite, potentially reducing the desire to consume excess calories following a workout.
Additionally, HIIT may have a positive influence on food cravings and emotional eating behaviors. Engaging in HIIT sessions regularly could potentially help individuals manage their food cravings and make more mindful food choices. By regulating appetite and cravings, HIIT may support individuals in achieving their weight loss or maintenance goals more effectively.
• HIIT can regulate hunger hormones like ghrelin and leptin
• HIIT may decrease overall appetite
• Intense nature of HIIT workouts can reduce desire to consume excess calories post-exercise
• HIIT can positively influence food cravings and emotional eating behaviors
• Regular HIIT sessions may help individuals manage food cravings
• By regulating appetite and cravings, HIIT can support weight loss or maintenance goals
The Psychological Benefits of HIIT
Participating in high-intensity interval training (HIIT) offers more than just physical benefits – it also provides various psychological advantages. The intense bursts of activity followed by short rest periods in HIIT sessions can lead to a sense of accomplishment and empowerment. This feeling of achievement can boost self-confidence and motivation, making individuals more likely to stick to their fitness routines and achieve their goals.
Furthermore, the fast-paced nature of HIIT workouts can serve as a powerful distraction from daily stressors and worries. Engaging in HIIT requires focus and concentration on the exercises, diverting attention away from negative thoughts and promoting mindfulness. This mental shift towards the present moment can help reduce anxiety and improve overall mental well-being, creating a positive feedback loop between physical and psychological health.
The Impact of HIIT on Body Composition

High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has gained popularity for its significant impact on body composition. Research has shown that HIIT can lead to improvements in lean muscle mass and reductions in body fat percentage. This is attributed to the intense nature of HIIT workouts, which can stimulate muscle protein synthesis and increase post-exercise oxygen consumption, ultimately aiding in fat loss and muscle gain.
Furthermore, HIIT has been found to enhance metabolic rate not only during the workout but also post-exercise due to excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). This means that the body continues to burn calories at an elevated rate even after the workout has been completed, contributing to further improvements in body composition. Additionally, the combination of aerobic and anaerobic elements in HIIT workouts can help maximize calorie expenditure and metabolic adaptations, making it an effective strategy for those looking to improve their body composition.
The Science Behind HIIT and Endurance
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has been shown to significantly improve endurance in individuals of varying fitness levels. The science behind this enhancement lies in the way HIIT workouts challenge the cardiovascular and respiratory systems to adapt and become more efficient over time. By alternating between intense bursts of exercise and short periods of rest or lower-intensity activity, HIIT pushes the body to work harder and improve its oxygen utilization, ultimately leading to enhanced endurance capacity.
Research has indicated that HIIT can stimulate the production of mitochondria in muscle cells, which are responsible for converting nutrients into energy. This increase in mitochondria density allows for improved energy production during prolonged physical activity, leading to enhanced endurance performance. Additionally, HIIT has been found to enhance the body’s ability to buffer lactic acid build-up, further contributing to improved endurance by delaying muscle fatigue.
The Role of Genetics in HIIT Adaptation
Genetics play a significant role in how our bodies respond and adapt to high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Research suggests that variations in certain genes can influence an individual’s aerobic capacity, muscle fiber composition, and overall fitness potential. For example, some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to respond more favorably to HIIT in terms of increasing their cardiovascular endurance and muscle strength.
Understanding how genetics impact HIIT adaptation can help tailor workout routines to better suit individual needs and goals. By identifying specific genetic markers related to fitness and exercise response, trainers and individuals alike can optimize their HIIT programs for improved performance and results. With advancements in genetic testing and personalized exercise programs, the role of genetics in HIIT adaptation is likely to become an increasingly valuable tool in maximizing the benefits of this popular training method.
How to Incorporate HIIT into Your Fitness Routine
When incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into your fitness routine, it’s important to start slowly if you’re new to this type of exercise. Begin with shorter intervals of high intensity followed by longer periods of rest or lower-intensity exercise. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your intervals as your fitness level improves. This progressive approach will help prevent injury and allow your body to adapt to the demands of HIIT.
To ensure you’re getting the most out of your HIIT workouts, it’s essential to focus on proper form and technique. Pay attention to your breathing, posture, and range of motion during each exercise. Engaging the correct muscles and performing movements with control will maximize the effectiveness of your HIIT routine. Additionally, remember to listen to your body and rest when needed to avoid overtraining and promote recovery.
The Future of HIIT Research and Development
As the popularity of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) continues to rise, the future of research and development in this area looks promising. Scientists and fitness experts are exploring new ways to optimize HIIT protocols for different populations, including beginners, athletes, and individuals with specific health conditions. With advancements in technology, researchers are also delving into the use of wearables and tracking devices to monitor and personalize HIIT workouts for maximum effectiveness.
Additionally, the future of HIIT research is likely to focus on further elucidating the physiological mechanisms behind the benefits of HIIT, such as fat oxidation, muscle building, and cardiovascular health. This deeper understanding can lead to the development of more targeted HIIT programs that cater to specific fitness goals and individual needs. Moreover, as the field of exercise science evolves, collaborations between researchers, health professionals, and industry experts are expected to drive innovation in HIIT methodologies and applications.













